Ethereum State Transition Function
Prerequisites
Ethereum State Machine
Ethereum is a distributed state machine. A state machine is a mathematical model of computation with two major components:
- the state, the configuration of the system at a moment in time
- a transaction, the set of instructions to change the state
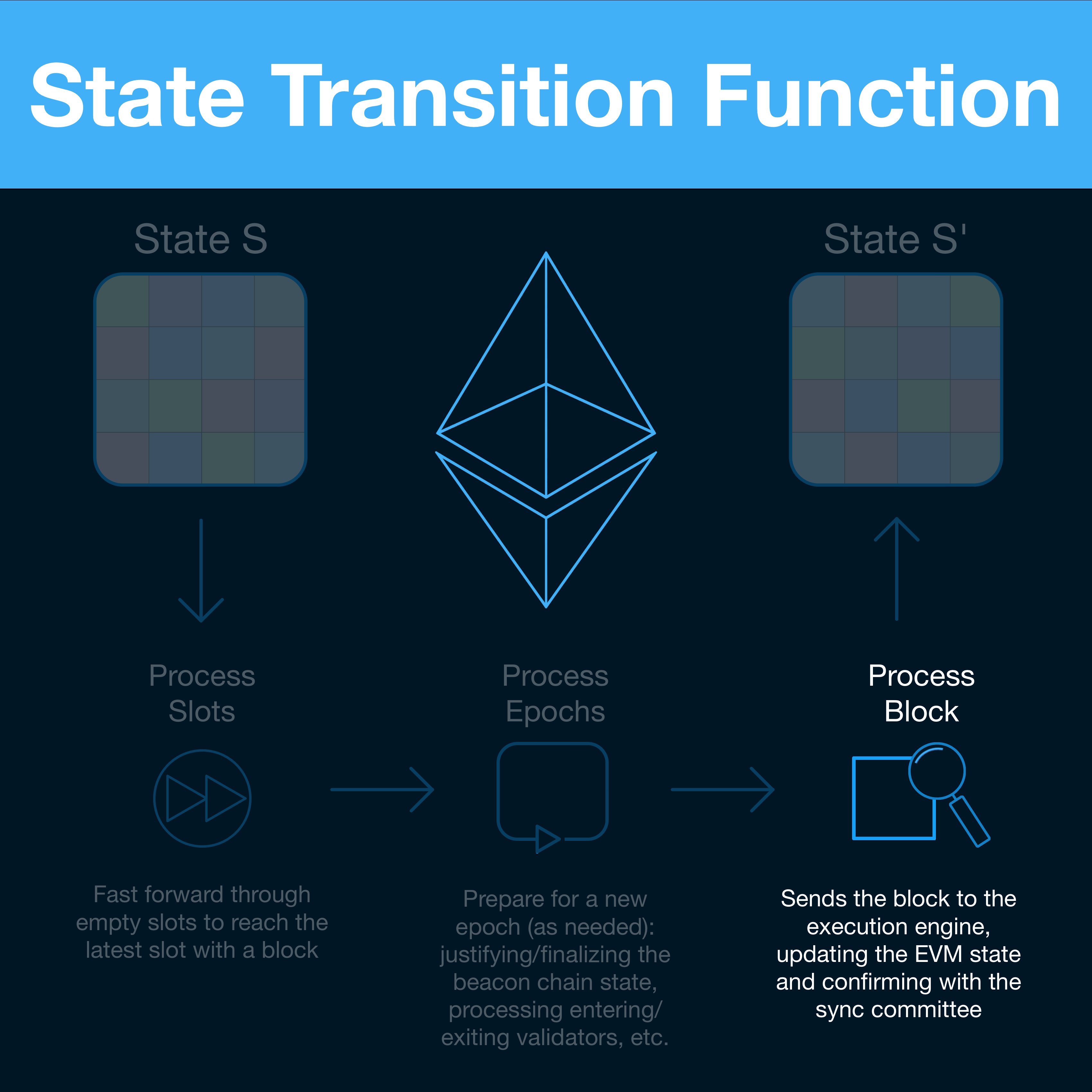
State Transition Function
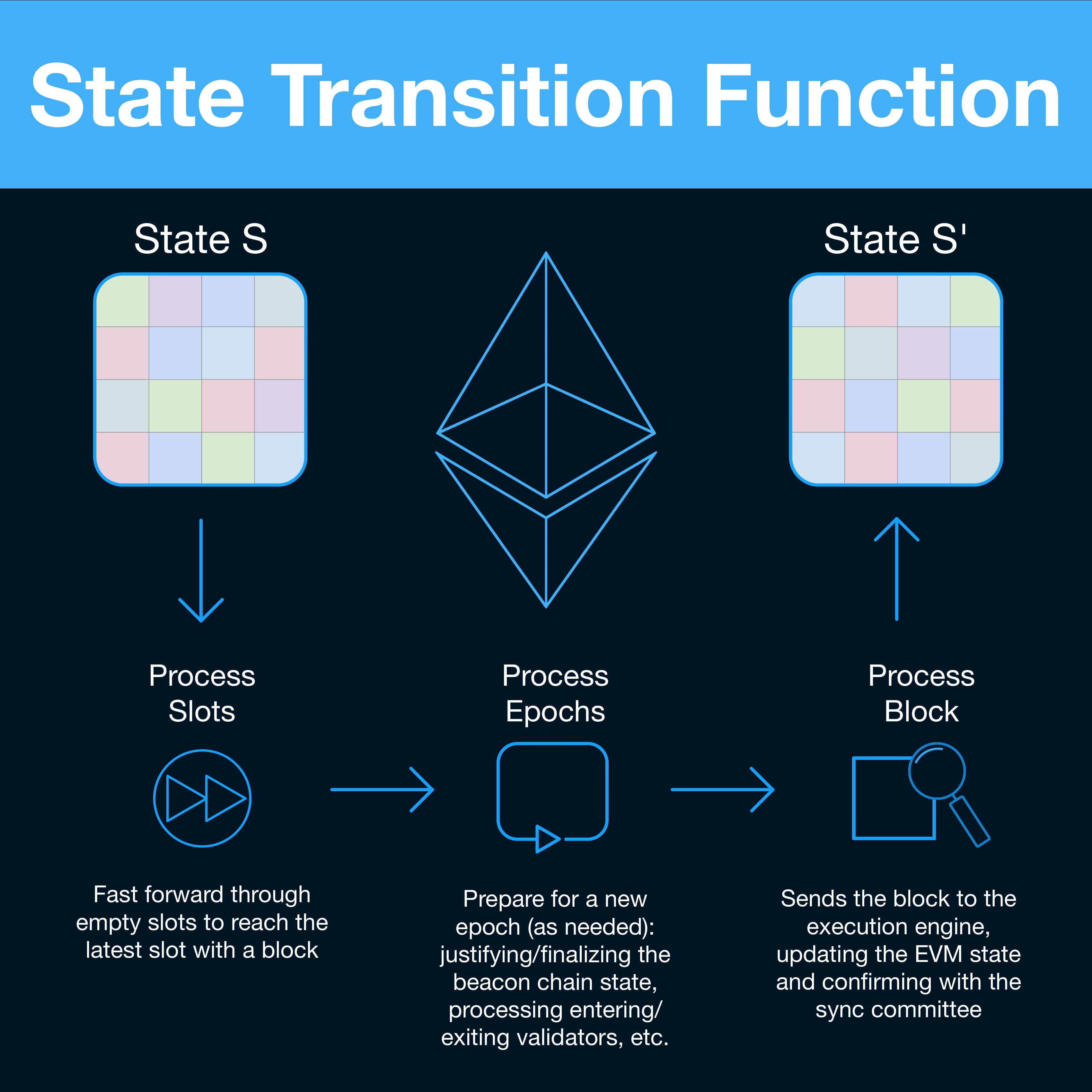
A state is a static snapshot in time, the transactions are the instructions to change the state and the state transition function is the mechanism that applies the transactions to the state.
- Inputs: current state, new block
- Output: new state
Ethereum Specification

First, process all the empty slots that do not have a block (process_slots).
Check the signature of the block (verify_block_signature) and if it's valid, process the block by executing the underlying transactions (process_block).
Process Slots
Sometimes a slot passes without a block being proposed; maybe the proposer was offline or the network dropped the block. The state transition function moves through empty slots and triggers a change of epoch, if needed.
- Inputs: current state, slot
- No output
Ethereum Specification
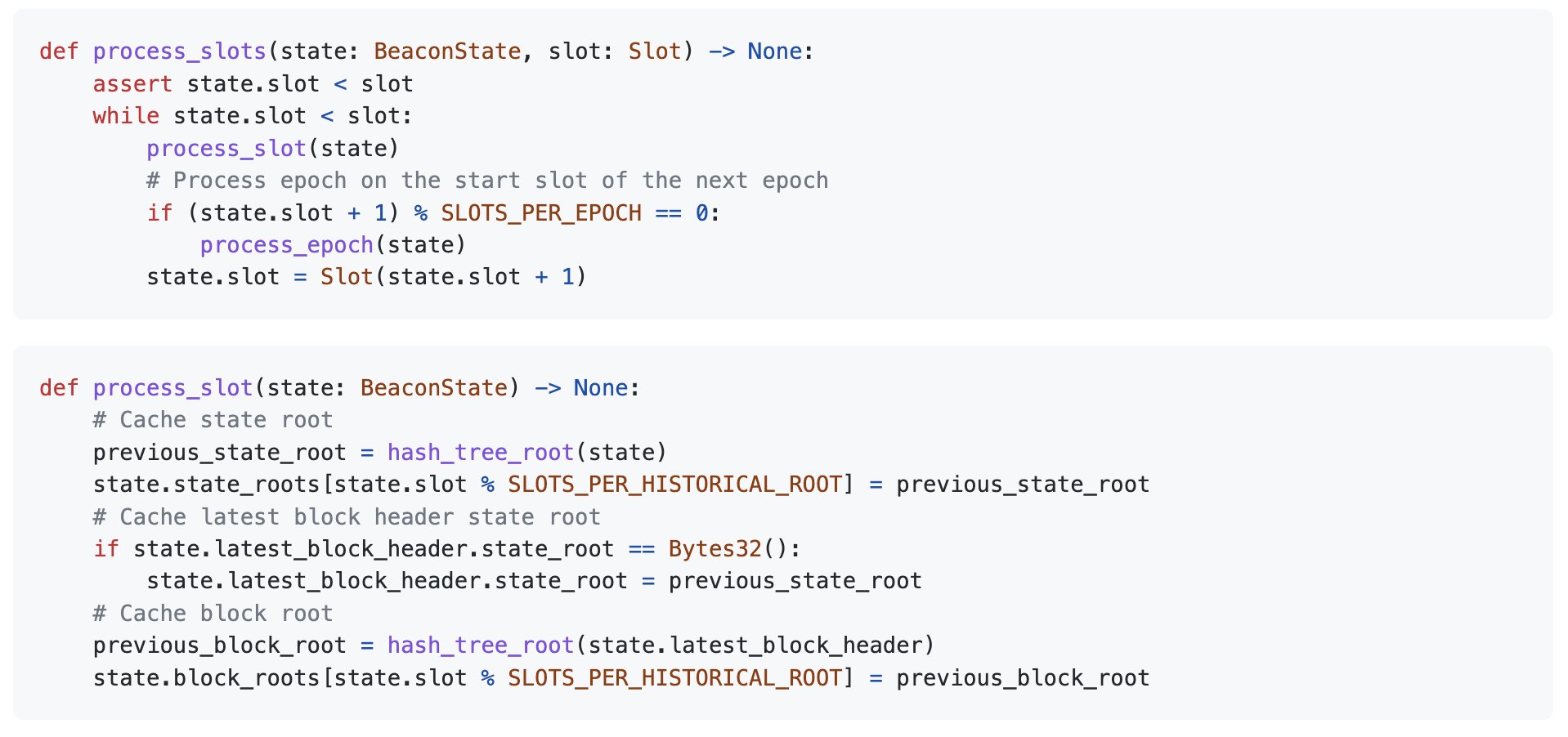
While the current slot is less than the intended slot, progress forward (process_slot).
If the next slot is going to be a new epoch, execute the processes associated with consensus and prepare for the next epoch (process_epoch).
Process Epochs
An epoch is 32 slots/blocks. When process_slots moves through this boundary, the validator must attend to many consensus-based and housekeeping duties.
- Input: current state
- No output
Ethereum Specification
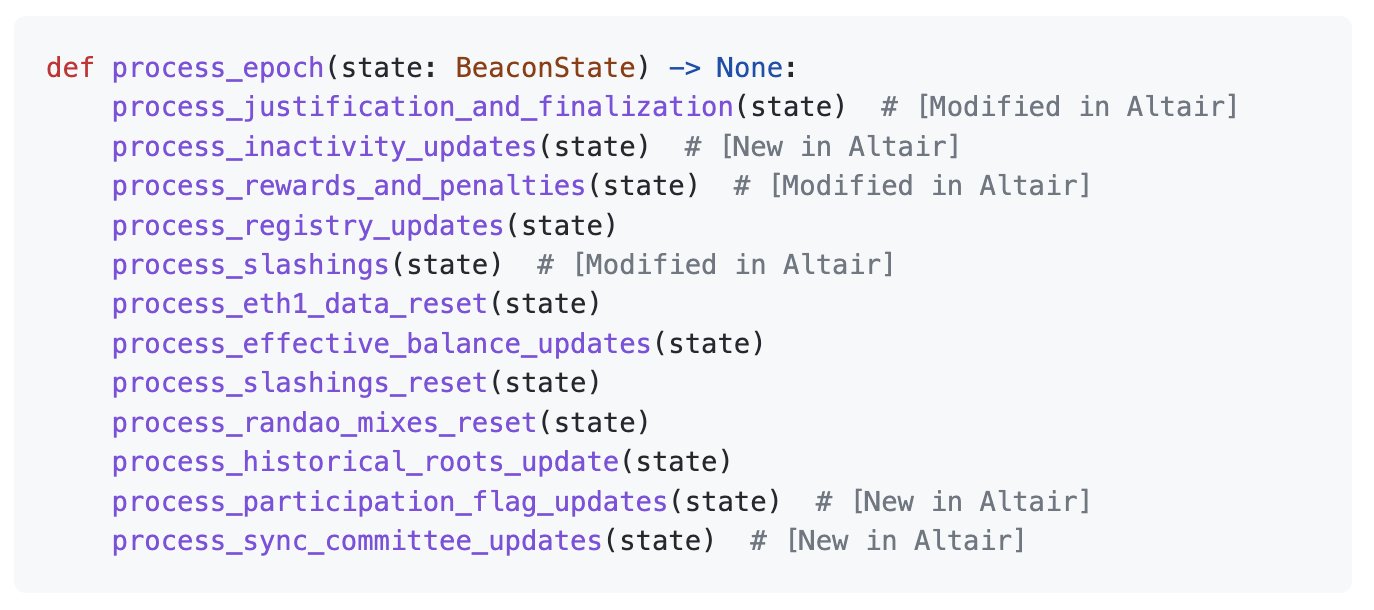
This is the consensus spec, as you can see it's very dense. Here's a summary of each step.

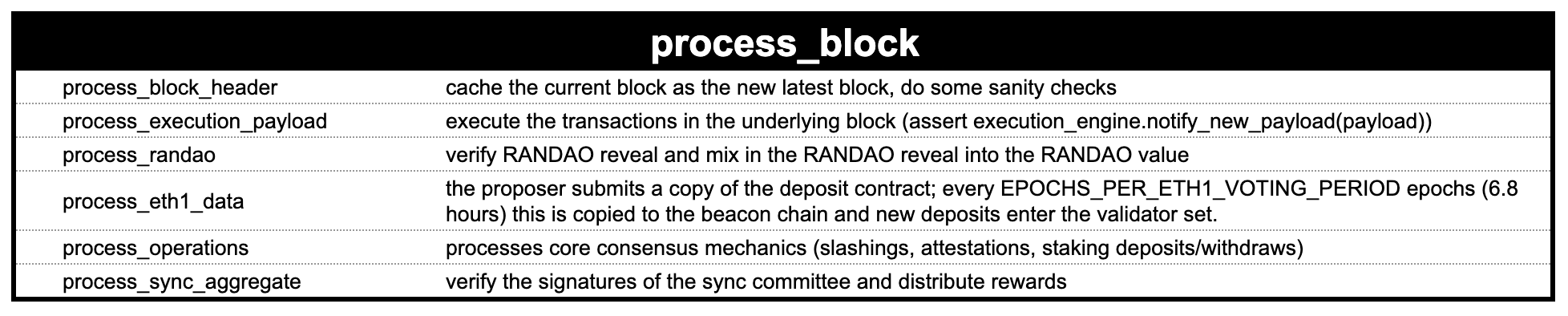
Process Block
Finally, we get to the good part; it's time to process the block!
Checking the header one more time, the validator will feed the block (and the transactions it carries) into the EVM. It ends with some consensus housekeeping.
- Inputs: current state, block
- No output
Ethereum Specification

At the core, the validator performs final checks (process_block_header) and feeds the block into the EVM (process_execution_payload).

The first chunk of this function is just more checks. The moment the validator passes the transactions to the EVM is execution_engine.notify_new_payload(payload).
Finally, the validator returns to its consensus duties (found in process_block). Here is a summary
Resources
The Best Semi-Technical Manual on Ethereum
Source Material - Twitter Link